The convenience and ease of online shopping have transformed the retail landscape. E-commerce has exploded in popularity, offering a vast selection of products delivered directly to our doorsteps. However, this surge in online shopping comes with a hidden cost – a growing mountain of electronic waste, or e-waste.
Key factors in the rise of ecommerce
Several factors have contributed to the meteoric rise of e-commerce:
- Convenience: Shopping online is convenient and accessible, allowing purchases anytime, anywhere.
- Competitive prices: E-commerce platforms often offer competitive pricing due to lower overhead costs compared to brick-and-mortar stores.
- Wider selection: Online retailers boast a wider variety of products compared to physical stores, catering to niche interests and global markets.
- Technological advancements: Improved internet infrastructure, user-friendly websites, and secure payment gateways have fueled e-commerce growth.
- The rise of mobile shopping: The ability to shop from smartphones and tablets further fuels the e-commerce revolution.
Environmental implications of increased online shopping
While e-commerce offers undeniable benefits, its environmental impact cannot be ignored. Here are some key concerns:
- Packaging waste: The massive amount of packaging materials used for online deliveries contributes significantly to solid waste generation. Cardboard boxes, plastic wrapping, and packing peanuts often end up in landfills.
- Rapid obsolescence: The fast-paced nature of technology leads to frequent product upgrades, resulting in discarded electronics with potentially usable components.
- Carbon emissions: E-commerce involves a complex supply chain, with transportation of goods from warehouses to customers generating greenhouse gas emissions.
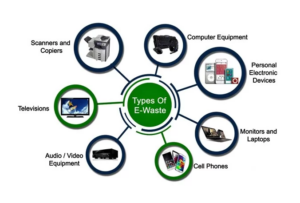
- E-waste generation: The rapid turnover of electronics and the lack of proper disposal methods lead to a surge in e-waste, which contains hazardous materials like lead, mercury, and flame retardants. Improper e-waste disposal poses a significant threat to human health and the environment.
- Return and disposal challenges: The ease of online returns can lead to increased waste, as unwanted items are often discarded instead of being properly refurbished or recycled.
Sustainable practices in ecommerce
There are ways to mitigate the environmental impact of e-commerce. Here are some sustainable practices businesses can adopt:
- Eco-friendly packaging: Utilizing biodegradable or recyclable packaging materials can significantly reduce waste.
- Product longevity: Designing durable and long-lasting products reduces the need for frequent replacements.
- Right-to-repair: Offering consumers the right to repair their electronics extends product lifespan and reduces e-waste.
- Take-back programs: Implementing take-back programs allows for responsible collection and recycling of used electronics.
- Carbon offsetting initiatives: Businesses can invest in carbon offsetting initiatives to compensate for their emissions.
- Promoting sustainable consumption: Educating consumers about responsible purchasing and e-waste disposal can make a significant difference.
Challenges and potential solutions in E-waste management
E-waste management presents several challenges:
- Complexity of E-waste: Electronic devices contain various materials, making them difficult and expensive to recycle properly.
- Lack of infrastructure: Many countries lack the infrastructure and technology necessary for efficient e-waste processing.
- Informal recycling practices: Informal e-waste recycling practices in developing countries pose health and environmental risks.
Potential solutions include:
- International collaboration: International cooperation can develop standardized e-waste management practices and support infrastructure development in developing countries.
- Producer responsibility: Holding manufacturers responsible for the end-of-life management of their products can incentivize sustainable design and recycling programs.
- Technological advancements: Investing in research and development of new e-waste recycling technologies can improve efficiency and profitability.
- Consumer awareness: Raising public awareness about the dangers of improper e-waste disposal and promoting responsible recycling habits is crucial.
Conclusion
The e-commerce revolution is here to stay, but it doesn’t have to come at the expense of our planet. Embracing sustainable practices throughout the entire e-commerce lifecycle, from product design to packaging and disposal, businesses can create a win-win situation for both the environment and their bottom line. Consumers also have a vital role to play in making informed purchasing decisions, choosing durable products, and properly disposing of e-waste, which collectively contribute to a more sustainable e-commerce ecosystem.
Calls-to-Action (CTA):
- For businesses:
- Audit your e-commerce operations to identify areas for improvement in terms of sustainability.
- Explore partnerships with organizations specializing in e-waste recycling and responsible disposal.
- Educate your customers about your sustainability efforts and encourage responsible e-waste disposal practices.
- For consumers:
- Research the environmental impact of the products you purchase before making a decision.
- Choose durable and long-lasting electronics whenever possible.
- Explore repair options for broken electronics before discarding them.
- Look for retailers offering take-back programs for used electronics.
- Educate yourself about responsible e-waste disposal options in your community.

