In an age where our online presence is ever-expanding and digital interactions are part of our daily routine, understanding the safety of the links we encounter is more crucial than ever. With cyber threats lurking around every corner, knowing whether a URL is secure can mean the difference between a seamless browsing experience and a potential security disaster. Navigating the vast web of information doesn’t have to be a perilous journey; with the right knowledge, you can confidently identify safe links and protect your personal information. In this complete guide, we’ll break down the essential elements of a secure URL, explore common red flags to watch out for, and provide practical tips for ensuring your online safety. Whether you’re a casual internet user or someone who spends hours online, this comprehensive resource will empower you to surf the web with confidence and peace of mind.
Understanding URL structure
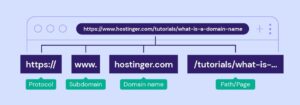
Understanding URL structure is fundamental to identifying secure links and protecting yourself while browsing the internet. A URL, or Uniform Resource Locator, is the address used to access resources on the web, and it consists of several key components that can reveal important information about its security.
At the beginning of every secure URL is the protocol, denoted as “https://” rather than just “http://”. The ‘s’ in ‘https’ stands for secure, indicating that the website uses encryption protocols such as SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) or TLS (Transport Layer Security). This encryption ensures that any data exchanged between your browser and the website is protected from eavesdroppers, making it a critical factor in assessing a link’s safety.
Following the protocol, you’ll find the domain name, which identifies the website’s owner. A well-known and reputable domain, such as “.gov” or “.edu”, typically suggests higher levels of trustworthiness. However, even commercial domains like “.com” can be secure, provided they adhere to best practices in web security.
Next comes the path, which directs you to a specific resource on the website. Here, it’s essential to note the presence of unusual characters or suspicious phrases that might indicate a phishing attempt. For instance, a legitimate URL usually avoids excessive numbers or obscure terms that seem irrelevant to the site’s purpose.
Lastly, pay attention to the URL length and complexity. While some sites may have longer URLs that are perfectly safe, excessively complicated URLs with random strings of letters and numbers could be a red flag. When evaluating a link, trust your intuition: if something feels off, it’s always best to err on the side of caution.
Understanding the risks
Before diving into the methods, it’s essential to understand the potential consequences of clicking on a malicious link:
- Phishing attacks: These scams aim to steal personal information by masquerading as legitimate websites or emails.
- Malware infection: Clicking on a malicious link can download harmful software onto your device.
- Data breaches: Malicious links can compromise your sensitive information, leading to identity theft.
- Financial loss: Phishing scams often target financial information, resulting in monetary losses.
Key indicators of a safe URL

When navigating the vast expanse of the internet, it’s essential to be able to identify safe URLs to protect yourself from potential threats. Here are some key indicators that can help you determine whether a link is secure:
1. Https protocol: One of the most visible signs of a secure URL is the presence of “https://” at the beginning of the link. The ‘s’ stands for secure, indicating that the website uses encryption to protect data exchanged between your browser and the site. Always prioritize URLs that start with https over http.
2. Padlock icon: Alongside the https protocol, look for a padlock icon in the address bar of your browser. This symbol signifies that the connection is secure. Clicking on this icon often provides more information about the site’s security certificate, confirming its legitimacy.
3. Domain name: Pay close attention to the domain name itself. Reputable websites often have clear and recognizable domain names. Be wary of misspellings or unfamiliar variations, which could indicate phishing attempts or fraudulent sites. For example, a site that mimics “paypal.com” but uses “paypa1.com” is likely malicious.
4. Contact information: A trustworthy website will typically provide clear contact information, including a physical address and customer service details. If this information is absent or difficult to find, it could be a red flag.
5. Privacy policy: Secure websites usually have a privacy policy that outlines how they collect, use, and protect user data. If you can’t find this information, consider it a warning sign about the site’s credibility.
6. Trust seals: Look for trust seals or badges from recognized security companies (like Norton, McAfee, or Better Business Bureau). These indicate that the site has undergone security checks and meets certain safety standards. However, be cautious—some malicious sites may falsely display these seals, so it’s wise to verify their authenticity.
7. Review and reputation: Before clicking on a link, do a quick search to check the website’s reputation. User reviews, ratings, and warnings from security software can provide invaluable insights into a site’s safety. If many people report negative experiences or if the site is flagged by antivirus programs, it’s best to steer clear.
How to spot a suspicious link?
- Hover over the link: Before clicking, hover your mouse over the link to see the full URL displayed in the bottom left corner of your browser. If the displayed URL doesn’t match the text of the link, it’s a red flag.
- Http vs. https: Security should be a top priority when sharing personal information online. URLs that begin with “http://” indicate a lack of encryption, while “https://” signifies that the website is secured with SSL encryption. Always look for that ’s’ in https, especially when entering sensitive data such as passwords or credit card information.
- Unusual domain extensions: While .com, .org, and .net are widely recognized, be cautious of unfamiliar domain extensions such as. xyz or. top. These can often be associated with less reputable sites. If a link uses an extension that seems odd or unfamiliar, take a moment to investigate its authenticity before proceeding.
- Look for misspellings or unusual characters: Typos, extra characters, or strange symbols in the URL are often signs of a phishing attempt.
- Beware of shortened links: Links shortened using services like Bitly or TinyURL can hide the actual destination. Be cautious when clicking on these unless you trust the sender.
- Urgent language: Scammers often use urgency to provoke hasty decisions. Phrasing such as “Act now!” or “Limited time offer!” can be clever tactics to push you into clicking on malicious links without thinking. Take a step back and evaluate the situation calmly before proceeding.
- Check the sender: If you received the link in an email, verify the sender’s identity and the legitimacy of the email. Be wary of unexpected emails or those with urgent requests.
- Trust your instincts: If something feels off or too good to be true, it probably is. Don’t hesitate to delete suspicious emails or messages without clicking any links.
Tools and resources for link safety
- URL checkers: Several online tools can scan links for malicious content. These services can provide valuable insights into the safety of a link before you click. An example is VirusTotal which scans URLs using multiple antivirus engines and website scanning services to detect any potential threats.
- Browser security: Modern web browsers offer built-in protection against phishing and malware. Keep your browser updated with the latest security patches.
- Antivirus software: A reliable antivirus program can help detect and block malicious links and files.
- Google safe browsing: Which allows you to check if a URL is associated with phishing, malware, or other security threats. Simply paste the link into the search box, and you’ll receive immediate feedback about its safety status.
- Web of Trust (WOT): Offers a user-friendly option. This extension displays a color-coded safety rating next to search results and links, allowing you to quickly identify whether a website is trustworthy based on community ratings and security checks.
- CheckShortURL: This tool expands shortened URLs, revealing the full link before you click, which can help you avoid potential scams or harmful sites.
- PhishTank: A community-driven platform that allows users to report phishing URLs. You can search the database to check if a suspicious link has been reported by others, providing an extra layer of protection against online threats.
Additional tips for online safety
- Be cautious on social media: Be wary of links shared by strangers or unfamiliar accounts.
- Avoid clicking on links in unsolicited emails or messages.
- Keep your software updated: Ensure your operating system and applications are up-to-date with the latest security patches.
- Use strong, unique passwords: Protect your accounts with strong, complex passwords and enable two-factor authentication whenever possible.
- Educate yourself: Stay informed about common internet scams and tactics used by cybercriminals. Familiarity with these techniques can empower you to recognize unsafe links and make informed decisions while browsing.
Conclusion
In today’s digital landscape, where every click can lead to a potential threat, empowering yourself with the knowledge to identify secure URLs is more crucial than ever. Master the art of discerning safe links to not only protect your personal information but also enhance your overall online experience. Remember, a secure URL is your first line of defense against phishing scams, malware, and other cyber threats.
As we’ve explored throughout this guide, key indicators such as the presence of https, padlock icons, and reputable domain names are essential checkpoints in your assessment process. Additionally, employing tools like URL scanners and being aware of common red flags can further fortify your defenses.
Take charge of your online safety by developing a habit of scrutinizing links before clicking. Share your newfound knowledge with friends and family, fostering a community of informed internet users. Ultimately, staying vigilant and informed is the best strategy to navigate the web securely. This not only safeguards your digital life but also contribute to a safer online environment for everyone. Stay alert, stay informed, and enjoy your time online with confidence!


Wonderful work! This is the kind of info that should bbe shared around
the net. Shame on the search engines for no longer positioning this publish higher!
Come on over and talk over with my site . Thank you =) https://66Bb4C96E165C.Site123.me/
Hello Monroe Williamson,
Thank you so much for your kind words 😊. We’re thrilled that you found our content helpful and worth sharing. We always strive to provide valuable insights and support for our community.
We’ll definitely keep pushing to ensure more people discover our resources. We also appreciate your invitation to check out your site – we’ll be sure to give it a visit! Thanks again for your encouragement and support
Warm regards,
Selly Africa