In an age where digital security breaches make headlines almost daily, the specter of cyberattacks looms large over businesses of all sizes. From high-profile retailers to multinational corporations, even the giants of the industry are not immune to the sophisticated tactics employed by cybercriminals. But what exactly happens behind the scenes of these breaches, and how can ordinary individuals and small businesses learn from these unsettling incidents? In this blog post, we will unveil the secrets of how big companies get hacked, exploring the vulnerabilities they expose and the strategies employed by hackers. More importantly, we’ll distill valuable lessons from these real-world examples, equipping you with practical insights to bolster your own cybersecurity defenses.
Common vulnerabilities in big companies
Cybercriminals employ a diverse arsenal of techniques to breach corporate defenses. Some of the most prevalent attack vectors include:
- Social engineering: Manipulating individuals to divulge confidential information or perform actions that compromise security. This encompasses phishing, spear phishing, and business email compromise (BEC) attacks.
- Malware and ransomware: Malicious software, including viruses, worms, and ransomware, is used to infiltrate systems, steal data, or hold systems hostage for ransom.
- Exploiting vulnerabilities: Hackers often capitalize on software weaknesses, such as zero-day exploits, to gain unauthorized access.
- Insider threats: Employees with malicious intent or accidental errors can pose significant risks to an organization’s security.
- Weak or stolen credentials: Reusing passwords, falling victim to phishing attacks, or poor password management can facilitate unauthorized access.
- Cloud misconfigurations: Improperly configured cloud services and applications can expose sensitive data and create vulnerabilities.
- Supply chain attacks: Targeting third-party vendors to infiltrate the supply chain and gain access to target organizations.
Tactics used by cybercriminals
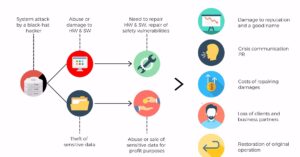
Cybercriminals have developed a cunning arsenal of tactics that they employ to infiltrate even the most secure systems. Understanding these methods is crucial not only for big corporations but also for individuals and smaller businesses looking to bolster their cybersecurity.
One of the most common tactics is phishing, where attackers send deceptive emails that appear legitimate, luring unsuspecting employees into clicking malicious links or divulging sensitive information. These emails often create a sense of urgency, urging recipients to act quickly—whether it’s resetting a password or confirming an account—making it all the more likely that they’ll fall victim to the scheme.
Another prevalent tactic is malware deployment. Cybercriminals often exploit vulnerabilities in software to install malware that can capture keystrokes, steal data, or grant unauthorized access to systems. Ransomware attacks have surged in popularity, where hackers encrypt a company’s data and demand a ransom for its release. This not only disrupts business operations but can also cause significant financial harm, as companies scramble to recover their data or comply with demands.
Social engineering is yet another method employed by cybercriminals, leveraging human psychology to manipulate individuals into breaking security protocols. This can occur in various forms, such as impersonating a trusted colleague or IT support to gain access to sensitive information.
Lastly, cybercriminals often use brute force attacks to crack passwords and gain unauthorized access to systems. Systematically attempting countless combinations, they exploit weak passwords, revealing the importance of robust password policies and multi-factor authentication.
The human factor: A critical vulnerability
While technological advancements have led to sophisticated cyberattacks, the human element remains a significant weak link. Employees are often the first line of defense, and their actions can either strengthen or weaken an organization’s security posture. Phishing attacks, for instance, heavily rely on social engineering tactics to deceive individuals into divulging sensitive information. Therefore, investing in employee cybersecurity awareness training is crucial.
Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs)
APTs are highly organized and persistent cyberattacks often conducted by nation-states or advanced criminal groups. These attacks are characterized by their long-term nature, targeting specific organizations for espionage or financial gain. APTs employ a combination of techniques, including social engineering, malware, and exploiting vulnerabilities, to infiltrate networks and extract valuable data.
Best practices for enhancing cybersecurity
In an era where cyber threats are increasingly sophisticated, adopting best practices for enhancing cybersecurity is essential for businesses of all sizes. Understanding how big companies get hacked exposes vulnerabilities that can be mitigated with proper strategies. Here are some key practices to bolster your cybersecurity posture:
- Implement strong password policies: Encourage the use of complex passwords and implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) to provide an extra layer of security. Regularly updating passwords and avoiding password reuse are fundamental steps in safeguarding sensitive information.
- Regular software updates: Keeping software, operating systems, and applications updated ensures that you benefit from the latest security patches. Cybercriminals often exploit vulnerabilities in outdated software, making regular updates a critical measure to thwart potential attacks.
- Conduct employee training: A company is only as strong as its weakest link. Regular cybersecurity training and awareness programs for employees can significantly reduce the risk of falling victim to phishing attacks and other social engineering tactics. Teach employees to recognize suspicious emails and to report any unusual activity immediately.
- Implement a robust firewall and antivirus solutions: Firewalls serve as a barrier between your internal network and external threats. Deploying reliable antivirus solutions can detect and neutralize malware before it compromises your systems.
- Backup data regularly: Maintaining regular backups of critical data ensures that you are prepared for any eventuality, such as ransomware attacks. Store backups securely and test their restoration process to confirm their integrity.
- Establish an incident response plan: Prepare for the worst by having a clear incident response plan in place. Define roles, responsibilities, and protocols to follow in the event of a cyber-attack. Quick and efficient responses can significantly minimize damage and recovery time.
- Limit access and permissions: Practice the principle of least privilege by giving employees only the access necessary for their roles. Regularly review access permissions and remove any that are no longer needed, especially when employees leave the company.
- Monitor and audit regularly: Continuous monitoring of network activity can help detect anomalies that may indicate a potential breach. Conducting regular security audits will help you identify and address vulnerabilities before they can be exploited.
Real-world case studies of major cyberattacks
Even the most sophisticated corporations are not immune to cyberattacks. Examining real-world case studies of major cyber incidents, we can uncover the vulnerabilities that led to these breaches and, more importantly, learn valuable lessons to fortify our own security measures.
One of the most infamous cases is the 2017 Equifax breach, where hackers exploited a vulnerability in a web application framework, exposing the personal information of approximately 147 million individuals. This incident highlighted the critical importance of timely software updates and the need for rigorous vulnerability management protocols. Equifax’s failure to patch a known vulnerability not only resulted in a massive data loss but also severely damaged its reputation, costing the company over $4 billion in total losses.
Another noteworthy example is the Target data breach of 2013, which saw hackers infiltrate the retailer’s network through compromised credentials from a third-party vendor. This incident underscored the risks associated with vendor relationships and the necessity for comprehensive security assessments of all partners. Target’s breach resulted in the theft of 40 million credit and debit card details and the personal information of an additional 70 million customers, leading to significant financial repercussions and a loss of consumer trust.
Then there’s the 2020 SolarWinds cyberattack, a sophisticated supply chain attack that affected thousands of organizations, including multiple U.S. government agencies. Hackers managed to insert malicious code into a legitimate software update, which was then distributed to customers. This case serves as a stark reminder of the vulnerabilities inherent in supply chain dependencies and the importance of implementing robust monitoring and detection strategies to identify anomalies in software behavior.
The importance of ongoing education and awareness
In a world where cyber threats are evolving at an unprecedented pace, the importance of ongoing education and awareness cannot be understated. Big companies often fall victim to hacking not just because of sophisticated attacks, but due to a lack of consistent training and awareness among their employees. Many high-profile breaches have exposed sensitive data, leading to financial loss and reputational damage, all stemming from human error or ignorance.
To combat this, organizations need to prioritize continuous education programs that keep employees updated on the latest security practices and potential threats. Regular training sessions, workshops, and simulations can foster a culture of vigilance and preparedness. Employees should be educated on the signs of phishing attempts, the significance of strong passwords, and the importance of data protection protocols.
Moreover, awareness campaigns can serve as powerful reminders of the risks associated with everyday actions, such as using unsecured networks or neglecting software updates. By creating an environment where employees feel empowered to report suspicious activities, companies can build a formidable defense against cyber intrusions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the alarming frequency of cyberattacks on big companies serves as a stark reminder that no organization, regardless of its size or stature, is immune to the threat of hacking. These incidents not only compromise sensitive data but also erode consumer trust and can lead to devastating financial repercussions. Examining the common vulnerabilities that hackers exploit, from outdated software and lax security protocols to social engineering tactics, we gain valuable insights into the importance of proactive cybersecurity measures.
As individuals and businesses, we must learn from these high-profile breaches and prioritize our own security strategies. Implementing robust security practices, such as regular software updates, employee training on phishing scams, and multi-factor authentication, can significantly reduce the risk of an attack. Moreover, fostering a culture of cybersecurity awareness within your organization is essential in creating a first line of defense against the evolving tactics employed by cybercriminals. Ultimately, while we can’t eliminate the risk of hacking entirely, we can certainly mitigate it through diligence, education, and the adoption of cutting-edge technology.

