In an increasingly digital world, where personal information is shared at the click of a button, the threat of data breaches looms larger than ever. With high-profile incidents making headlines, it can be easy to dismiss these breaches as distant concerns, but the reality is that they can happen to anyone—and often do. When your sensitive information is compromised, the consequences can be far-reaching, impacting not just your financial security but also your personal peace of mind. From identity theft to unauthorized access to your accounts, understanding the mechanics of data breaches is essential for safeguarding your privacy. We will look into what exactly happens during a data breach, the potential risks associated with compromised information, and most importantly, how you can protect yourself in this ever-evolving digital landscape.
 What is a data breach?
What is a data breach?
A data breach refers to an incident where unauthorized individuals gain access to confidential or sensitive information, typically held by organizations or individuals. This breach can occur through various means, including cyberattacks, system vulnerabilities, or even simple human error, such as misplacing devices that contain private data. The compromised information often includes personal details like names, social security numbers, financial information, and login credentials, which can have serious consequences for the affected parties.
The repercussions of a data breach can be far-reaching. For individuals, it may lead to identity theft, financial loss, and an erosion of personal privacy. For businesses, the fallout can be even more severe, resulting in reputational damage, legal liabilities, and financial penalties. Moreover, organizations may face costs related to notifying affected individuals, providing credit monitoring services, and implementing enhanced security measures to prevent future breaches.
Understanding what constitutes a data breach is crucial in today’s digital landscape, where personal and sensitive information is increasingly stored online. As technology continues to evolve, so too do the tactics employed by cybercriminals, highlighting the importance of vigilance, robust security practices, and the need for organizations and individuals alike to take proactive steps to safeguard their data. Awareness of the nature and implications of data breaches can empower everyone to take the necessary precautions to protect their information in an interconnected world.
Types of data breaches
Database breaches: Involving the theft of customer information, financial data, or employee records.
Cloud data breaches: Targeting cloud-based storage services and applications.
Email breaches: Compromising email accounts for phishing, data theft, or business email compromise (BEC).
Payment card breaches: Targeting payment card information for fraudulent transactions.
Intellectual property theft: Stealing trade secrets, patents, or proprietary information.
The breach lifecycle
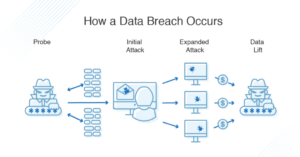
- Reconnaissance: This is the initial phase where attackers gather information about their target. They study the organization’s website, social media, employees, and other publicly available data to identify potential vulnerabilities.
- Intrusion: Once sufficient information is gathered; attackers attempt to penetrate the organization’s network. Common methods include phishing, exploiting vulnerabilities, or using stolen credentials.
- Lateral movement: After gaining initial access, attackers move laterally within the network to expand their control. They may access other systems, servers, and databases.
- Data exfiltration: The ultimate goal is to steal data. Attackers copy sensitive information to external storage or transmit it to a remote location.
- Covering tracks: To avoid detection, attackers often delete logs, modify system files, and implement backdoors for future access.
Common causes of data breaches
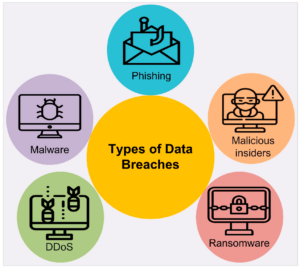
Data breaches have become an unfortunate reality in our increasingly digital world. Understanding the common causes of these incidents can empower individuals and organizations to better protect their sensitive information.
Phishing attacks: These deceptive tactics involve cybercriminals sending emails or messages that appear to be from legitimate sources, tricking recipients into revealing their personal information or login credentials.
Weak passwords: Many individuals and businesses still rely on easily guessable passwords, making it simple for hackers to gain unauthorized access to accounts. This is compounded by the practice of reusing passwords across multiple platforms, which can lead to widespread compromise if just one account is breached.
Inadequate security measures: Organizations that fail to implement robust cybersecurity protocols, such as firewalls, encryption, and regular software updates, leave themselves vulnerable to breaches.
Insider threats: Where employees intentionally or unintentionally expose sensitive data—can significantly heighten the risk.
External attacks: Such as ransomware and malware infections that exploit system vulnerabilities. Cybercriminals utilize these malicious tools to infiltrate systems, encrypt data, and demand ransom, resulting in both financial loss and data exposure.
The impact of a data breach on individuals
A data breach can have far-reaching and often devastating effects on individuals whose personal information is compromised. When sensitive data—such as Social Security numbers, credit card information, or medical records—falls into the wrong hands, the repercussions can be immediate and severe.
One of the most immediate impacts of a data breach is identity theft, where criminals use stolen information to impersonate victims. This can lead to unauthorized transactions, ruined credit scores, and the laborious process of recovering one’s identity. Victims may find themselves locked in a relentless battle with credit agencies and financial institutions, trying to rectify errors caused by fraudulent activity, which can take months or even years to resolve.
Additionally, the emotional toll of a data breach cannot be overstated. Victims often experience heightened anxiety, stress, and a lingering sense of vulnerability after their personal information has been compromised. The fear of being targeted again can lead to sleepless nights and a constant state of worry about financial security.
Moreover, the implications of a data breach extend beyond individual victims. When personal information is compromised, it can lead to a loss of trust in companies and organizations that fail to protect sensitive data. This erosion of trust can affect personal relationships and interactions with businesses, as individuals become more cautious about sharing their information.
Furthermore, individuals may face financial hardships as a result of a data breach. Some may incur unexpected costs related to credit monitoring services, legal fees, or even the need for therapy to cope with the emotional aftermath.
Steps to take after your information is compromised
Experiencing a data breach can be unsettling, leaving you feeling vulnerable and anxious about the security of your personal information. However, taking swift and appropriate action can significantly mitigate the potential damage. Here are essential steps to take after your information has been compromised:
1. Stay calm and assess the situation: The first step is to stay composed. Determine what specific information has been compromised and from which accounts. This will help you prioritize your next steps.
2. Change your passwords: Immediately update passwords for any affected accounts. Use strong, unique passwords that combine letters, numbers, and symbols. Consider utilizing a password manager to help generate and store complex passwords securely.
3. Monitor your accounts: Keep a close eye on your financial accounts, including bank statements and credit card transactions. Look for any suspicious activity and report it to your bank or credit card issuer immediately.
4. Enable two-factor authentication: For added security, enable two-factor authentication (2FA) on your accounts wherever possible. This provides an extra layer of protection by requiring a second form of verification in addition to your password.
5. Notify relevant parties: If your information was compromised in a way that affects your finances or identity, notify the relevant institutions, such as your bank, credit card companies, or any other entities that hold your sensitive information.
6. Consider a credit freeze or fraud alert: Placing a credit freeze on your accounts makes it more difficult for identity thieves to open new accounts in your name. Alternatively, you can set up a fraud alert, which notifies creditors to take extra steps to verify your identity before issuing new credit.
7. Check your credit reports: Obtain free copies of your credit reports from the major credit bureaus. Review them for any irregularities or accounts that you don’t recognize. Under U.S. law, you’re entitled to one free report from each bureau every year.
8. Report to authorities: If you suspect identity theft, file a report with your local police department and the Federal Trade Commission (FTC). This can provide you with documentation should you need to prove that your identity has been compromised.
9. Stay informed and educated: Learn about the latest scams and data breach trends to better protect yourself in the future. Awareness is a key component in safeguarding your personal information.
10. Consider identity theft protection services: If you find yourself feeling overwhelmed, it might be beneficial to invest in identity theft protection services. These services can monitor your accounts and alert you to any suspicious activity.
Preventative measures to protect your data
In an increasingly digital world, taking proactive steps to protect your personal information from data breaches is essential. While it may not be possible to eliminate all risks, implementing a combination of preventative measures can significantly reduce your vulnerability.
Employee training: Educating employees about cyber threats is crucial.
Strong password policies: Enforcing complex and unique passwords.
Multi-factor authentication (MFA): Adding an extra layer of security.
Regular software updates: Keeping systems and applications patched.
Incident response plan: Having a well-defined plan to respond to a breach.
Data encryption: Protecting sensitive data with strong encryption.
Regular security audits: Identifying and addressing vulnerabilities.
In conclusion, understanding data breaches and their implications is more crucial than ever. As we’ve explored, a data breach can compromise not only personal information but also your financial security and overall peace of mind. The aftermath of such an incident can be daunting, but there are proactive steps you can take to safeguard yourself. Staying informed about the latest security practices and potential threats is vital in arming yourself against future breaches. Regularly updating your passwords, utilizing two-factor authentication, and monitoring your accounts for suspicious activity are essential habits to adopt.
Moreover, being vigilant about the information you share online and understanding the privacy policies of the platforms you use can significantly reduce your risk. Knowledge is power; by educating yourself about cybersecurity and remaining alert to potential threats, you can better protect your personal information.